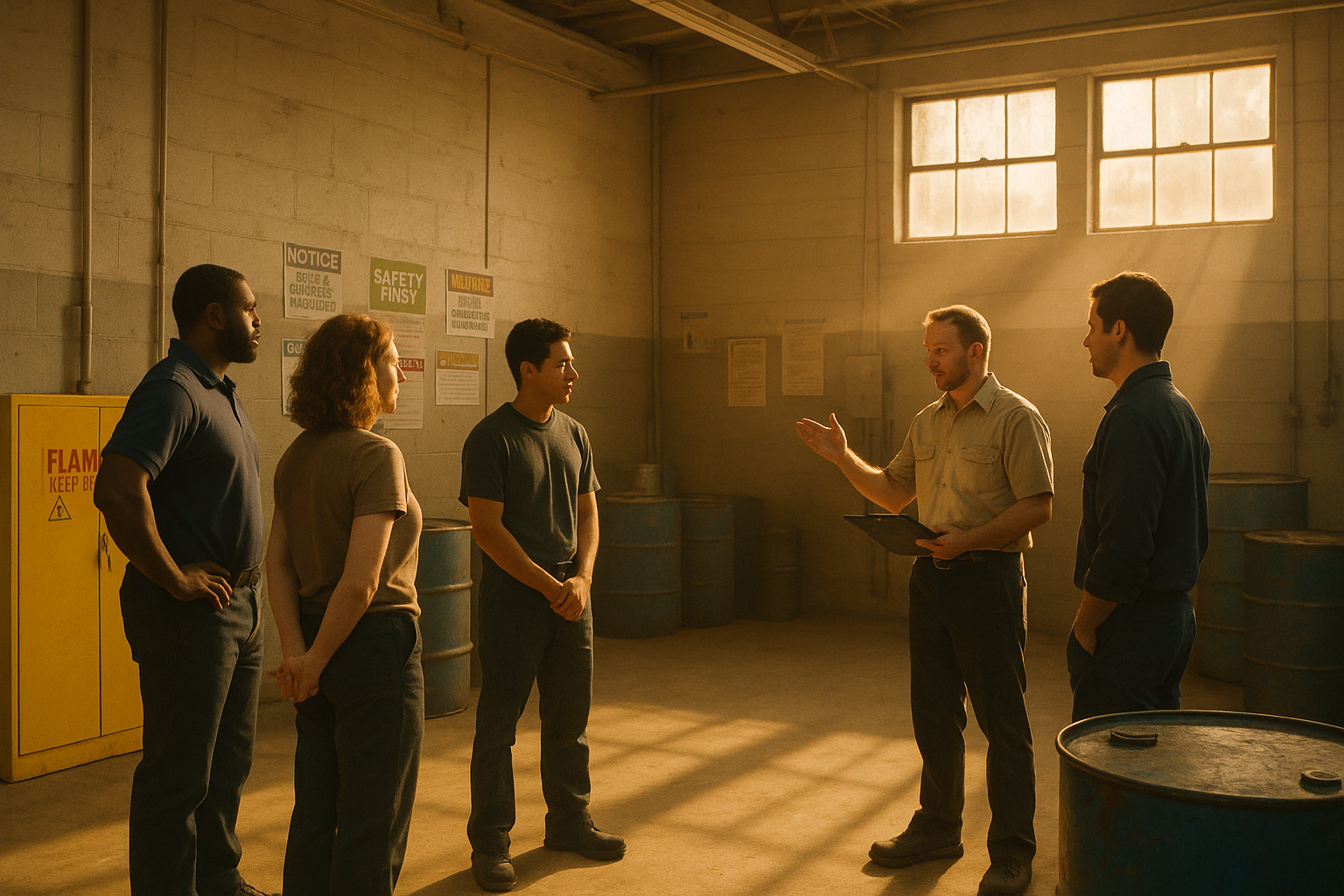
This course is designed for all general industry employees — including full-time, temporary, and contract workers.
Our goal is simple: prevent injuries from slips, trips, and falls, which remain a leading cause of serious injuries and fatalities in the workplace.
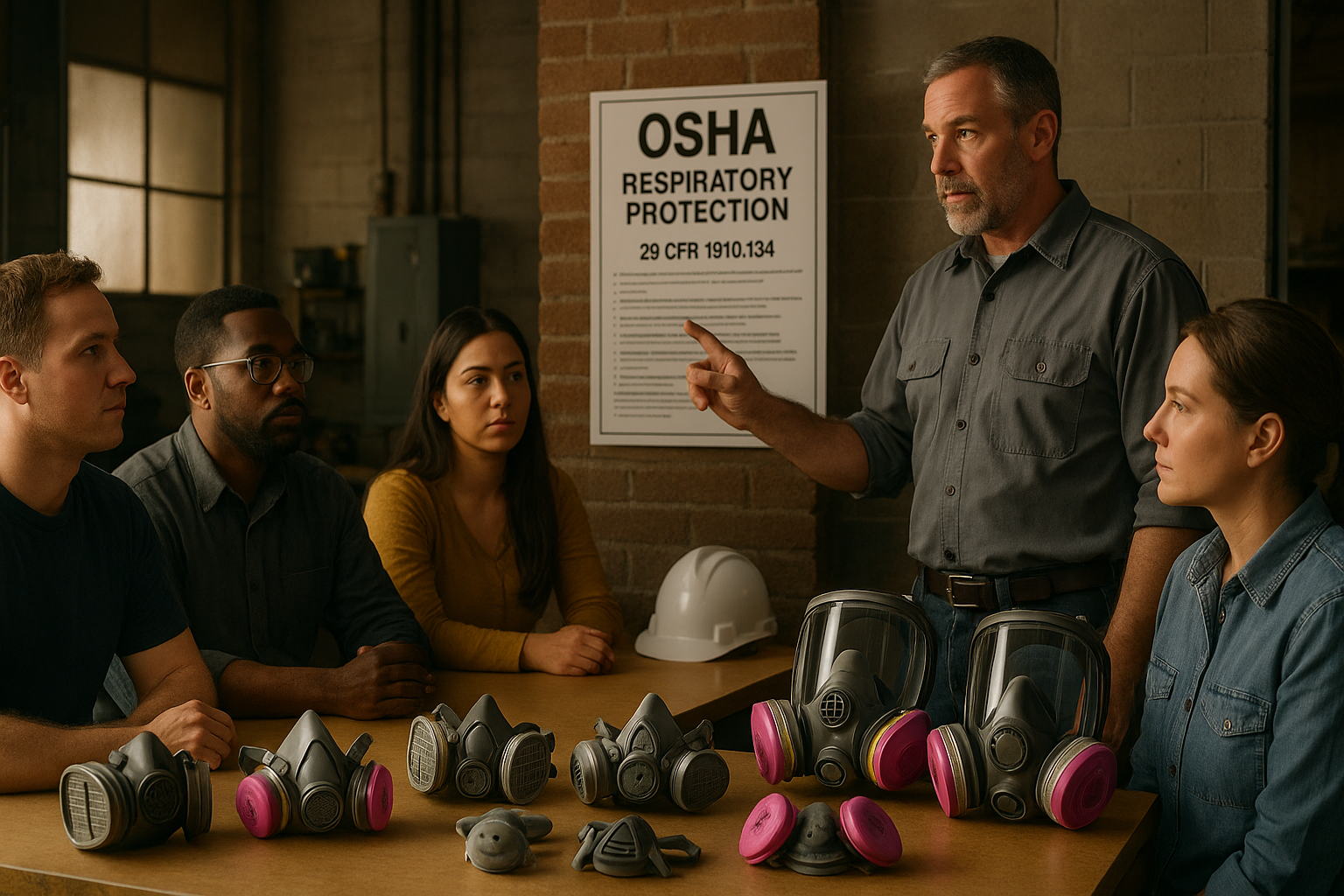
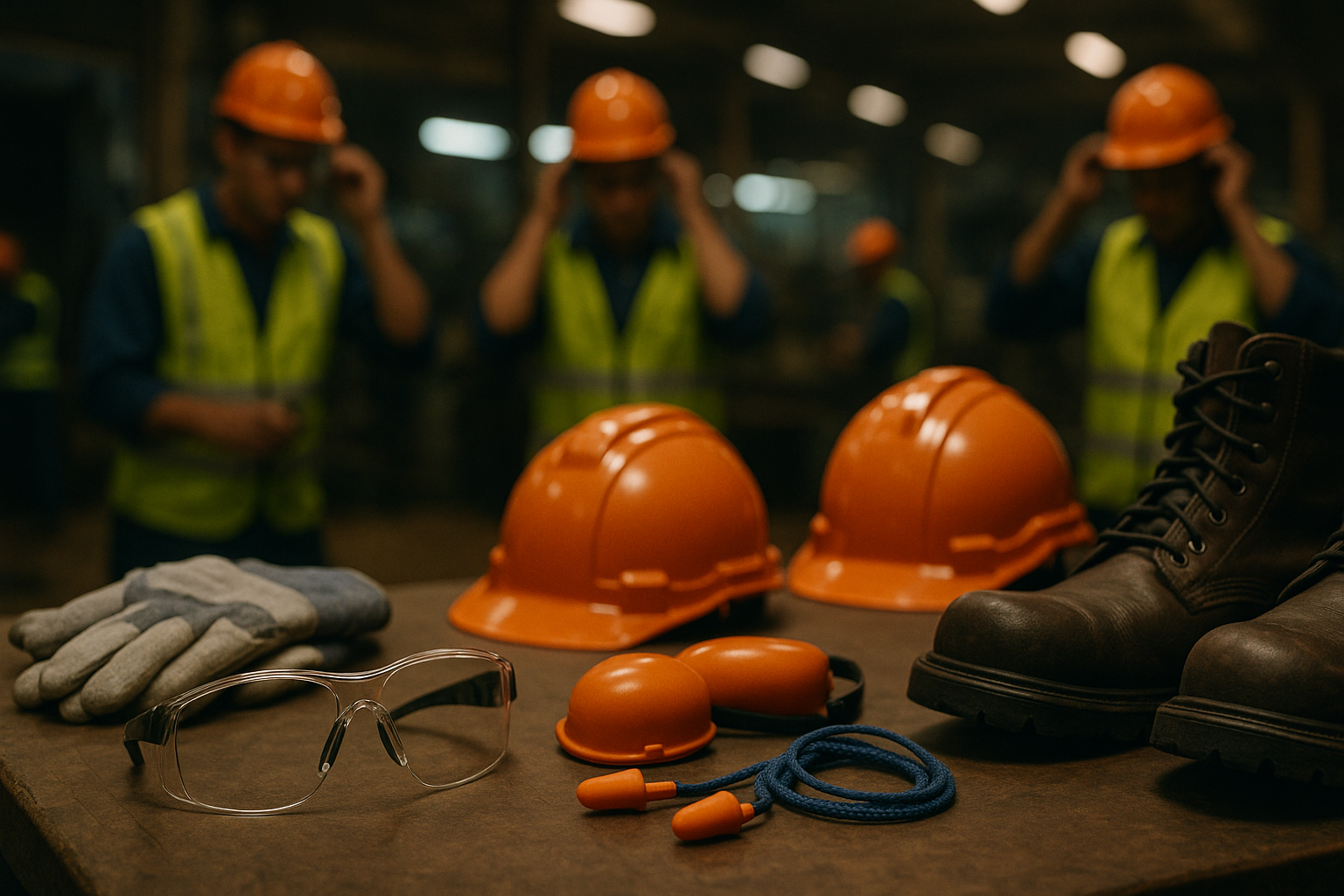
You’ll learn how to identify fall hazards, apply safe practices, and correctly use fall protection equipment in line with OSHA standards and our company’s safety program.
- Teacher: Robert Chamblee